Description
The high-moisture pelleting process developed at Idaho National Laboratory eliminates the energy-intensive drying step in pellet production. In this process, feedstock is size reduced and pelleted at a high moisture content prior to drying using a low energy drying method. A higher percentage of moisture was removed during preprocessing steps (size reduction and pelleting) than during preprocessing after drying. It has been shown to reduce the preprocessing cost by about 40% compared with the low-moisture pelleting method followed by the industry. Eliminating the high-temperature drying step in pellet production reduces the volatile organic compound emissions and also makes pelleting more environmentally friendly.
Capability Bounds
High moisture pelleting has been tested on various types of feedstock (corn stover, Douglas fir, Pine, MSW, Miscanthus, Switchgrass, Sorghum, Wheat Straw), and at various moisture contents up to nearly 30% w.b. moisture content.
Unique Aspects
Reductions in greenhouse gas emissions of up to 40% have also been modeled through the reduction in usage of high temperature drying methods.
Availability
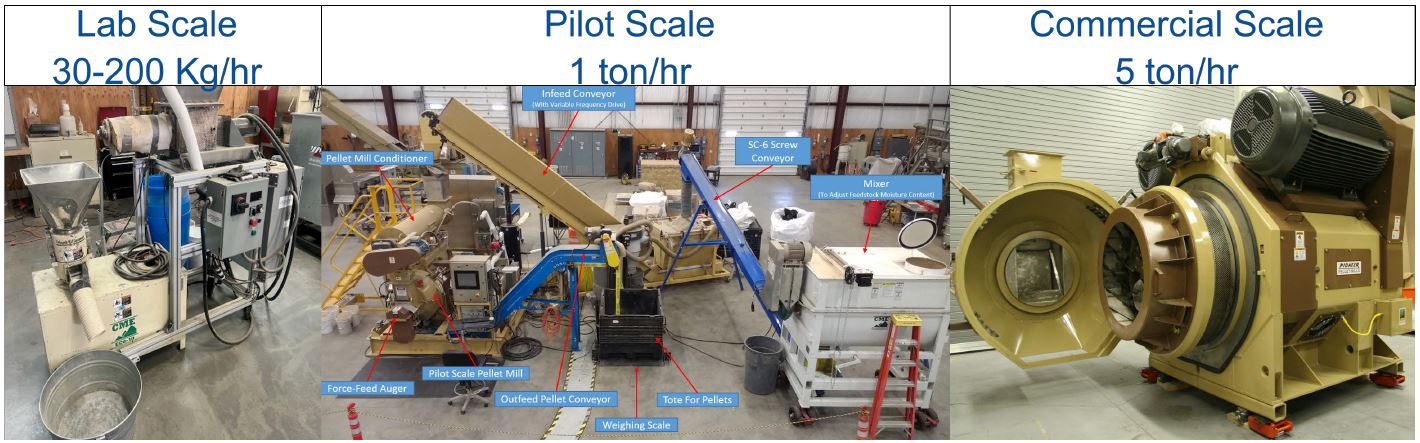
Capabilities and availability of high moisture pelleting is available at the Idaho National Laboratory at 3 scales (lab scale kg/hr, pilot scale 1 ton/hr, and commercial scale 5 ton/hr) through the Biomass Feedstock National User Facility with the through the development of collaborative work scopes that utilize a variety of contractual mechanisms to meet the needs of the partners and funding agencies.
Benefit
Reduction in preprocessing costs and greenhouse gas emissions are possible with High moisture pelleting.
Capability Expert(s)
Zachary Smith, Neal Yancey
References
Smith, Zachary, et al. “Grinding and Pelleting Characteristics of Municipal Solid Waste Fractions.” Energies 17.1 (2023): 29.
Tumuluru, Jaya Shankar. “High‐moisture pelleting of corn stover using pilot‐and commercial‐scale systems: Impact of moisture content, L/D ratio and hammer mill screen size on pellet quality and energy consumption.” Biofuels, Bioproducts and Biorefining 17.5 (2023): 1156-1173.
Tumuluru, Jaya Shankar. “Effect of process variables on the density and durability of the pellets made from high moisture corn stover.” Biosystems engineering 119 (2014): 44-57.
Tumuluru, Jaya Shankar. “High moisture corn stover pelleting in a flat die pellet mill fitted with a 6 mm die: physical properties and specific energy consumption.” Energy Science & Engineering 3.4 (2015): 327-341.
Tumuluru, Jaya Shankar. “Effect of pellet die diameter on density and durability of pellets made from high moisture woody and herbaceous biomass.” Carbon Resources Conversion 1.1 (2018): 44-54.
